The Process of Respiration (Part - 2)
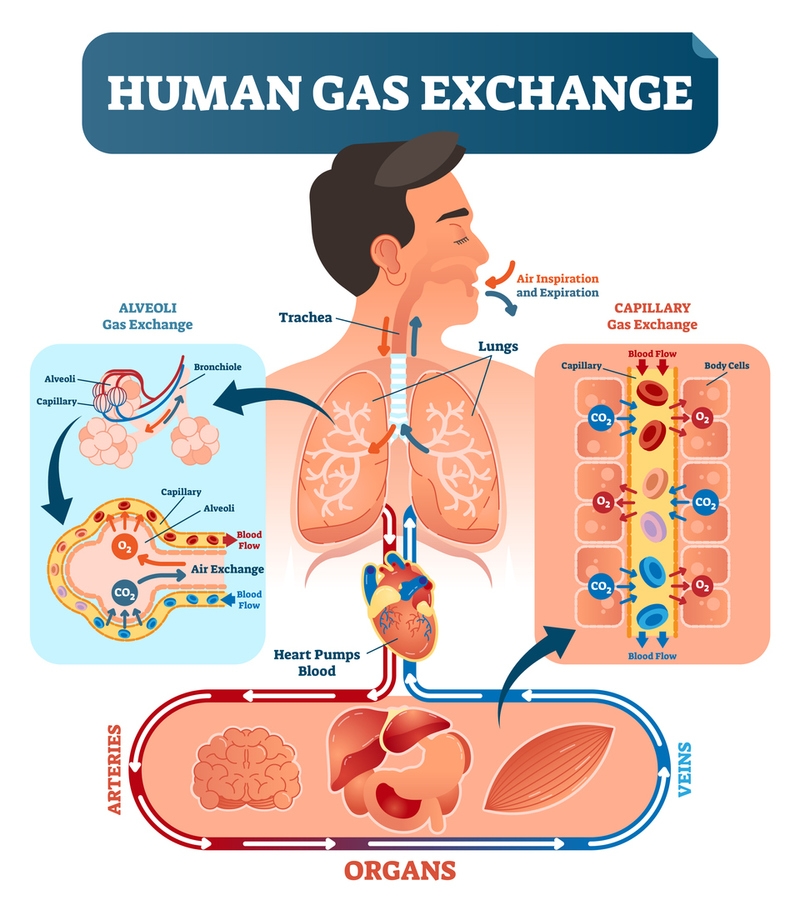
The lungs are the site for exchange of gases. Lungs are present in the chest cavity or thorax cavity.The lungs are protected by brist bone/chest bone/sternum from the front, rib cage from sides and back bone or vertebral column from back. When we breathe in our lungs expand, moving ribs outward. When we breathe out our lungs contract, moving ribs inward.
At the bottom of the lungs a structure called diaphragm is present, which helps the lungs to expand and contract properly. Not only that, they also stop lungs from damaging the stomach. When we breathe in the diaphragm moves downward and when we breathe out they move inward. The diaphragm is also called the floor of chest cavity as it is the bottom most structure of the chest cavity.
The oxygenated blood from the heart is supplied to almost all the cells by blood vessels. The end of the blood vessel is a blood cappillary, which connects to the cell. When the blood reaches the cells, oxyhemoglobin converts to hemoglobin and oxygen. The CO2 from cell forms carbomino-hemoglobin when it combines with hemoglobin. This blood is taken back to the heart then to lungs for oxygenation.
The energy in our body is produced by respiration. The respiration is of two types - aerobic and anaerobic respiration. The aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of oxygen. In this process the substances are completely oxidised. And the energy produced is huge (38 molecules of ATP or 686 kilo cal. of energy). The end products are carbon dioxide and water vapour.
The chemical equation of aerobic respiration goes as follows:
C6 H12 O6 + 6 O2 = 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 38 molecules of ATP
The another type of respiration is anerobic respiration. This process occurs when there is an oxygen debt (shortage of oxygen) in our body. This process also occurs in lactobacillus bacteria, yeast and a few other organisms. Here, there is no need of oxygen. The substances are not completely oxidised. A little amount of energy is produced (2 molecules of ATP or 56 kilo cal. of energy). The end products are CO2 and lactic acid or ethyl alcohol.
There are two types of anerobic respiration - lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation. Lactic acid fermentation occurs only in lactobacillus bacteria, here the glucose or fatty acid is broken down to lactic acid. Alcoholic fermentation occurs in humans as well as yeasts, here the glucose or fatty acid is converted to ethyl alcohol.
The chemical equation of anerobic respiration (alcoholic fermentation) goes as follows:
C6 H12 O6 = 2 CO2 + 2 C2 H5 OH + 2 mol of ATP
Did you know: frogs breathe through skin (cutaneous respiration), lungs (pulmonary respiration), mouth and nose (buccopharyngeal respiration), gills at larvae stage (bronchial respiration). Where as scorpions and crabs breathe through book lungs.
- Blog by Daksh Bawgiker

Comments
Post a Comment